France, a welcoming home for mathematicians
With 13 Fields Medals, 1 Gauss Prize and 5 Abel Prizes to their name, the work of French researchers is widely recognised internationally. There are around forty French mathematical journals, some of which are among the best published internationally.
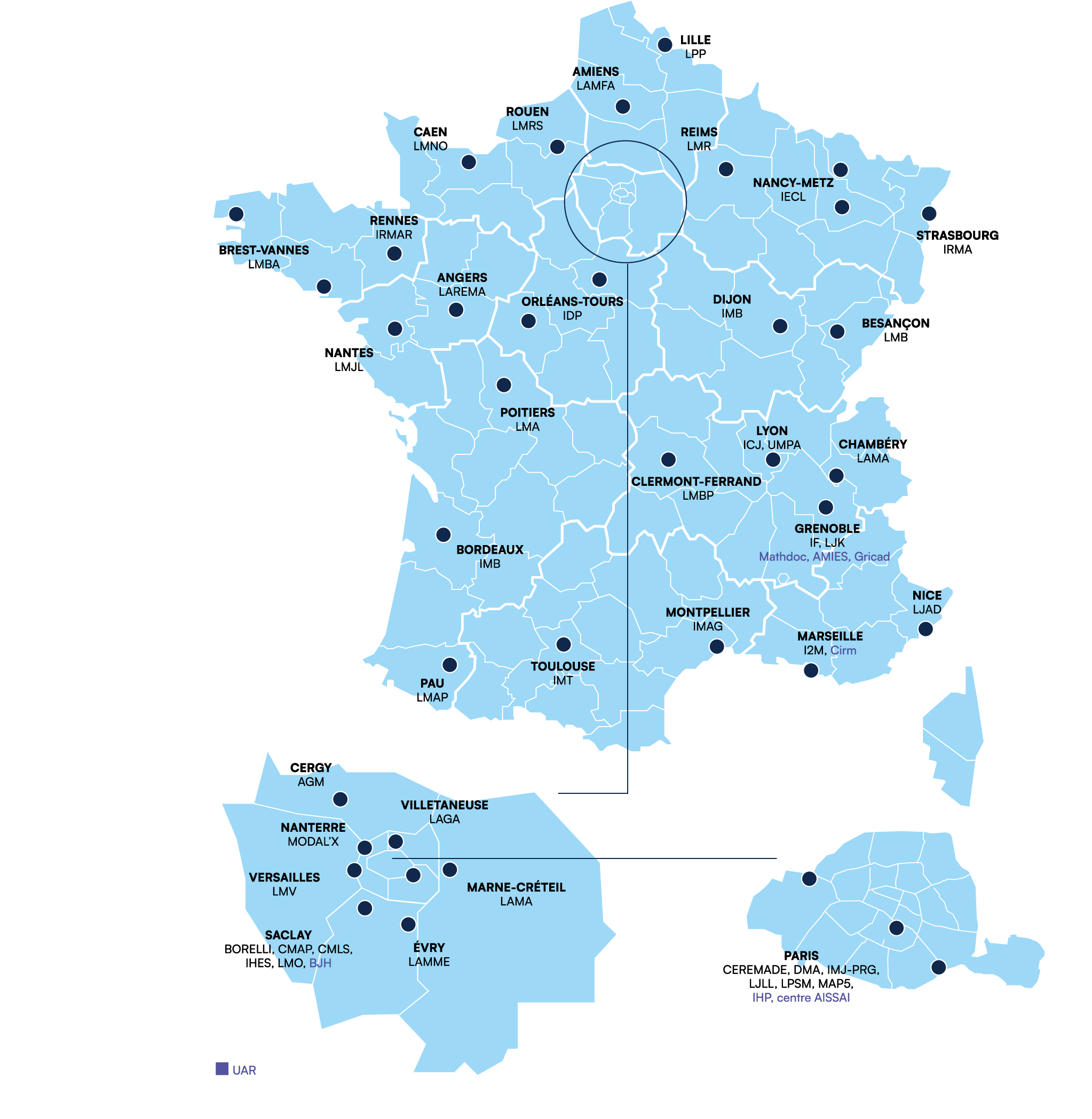
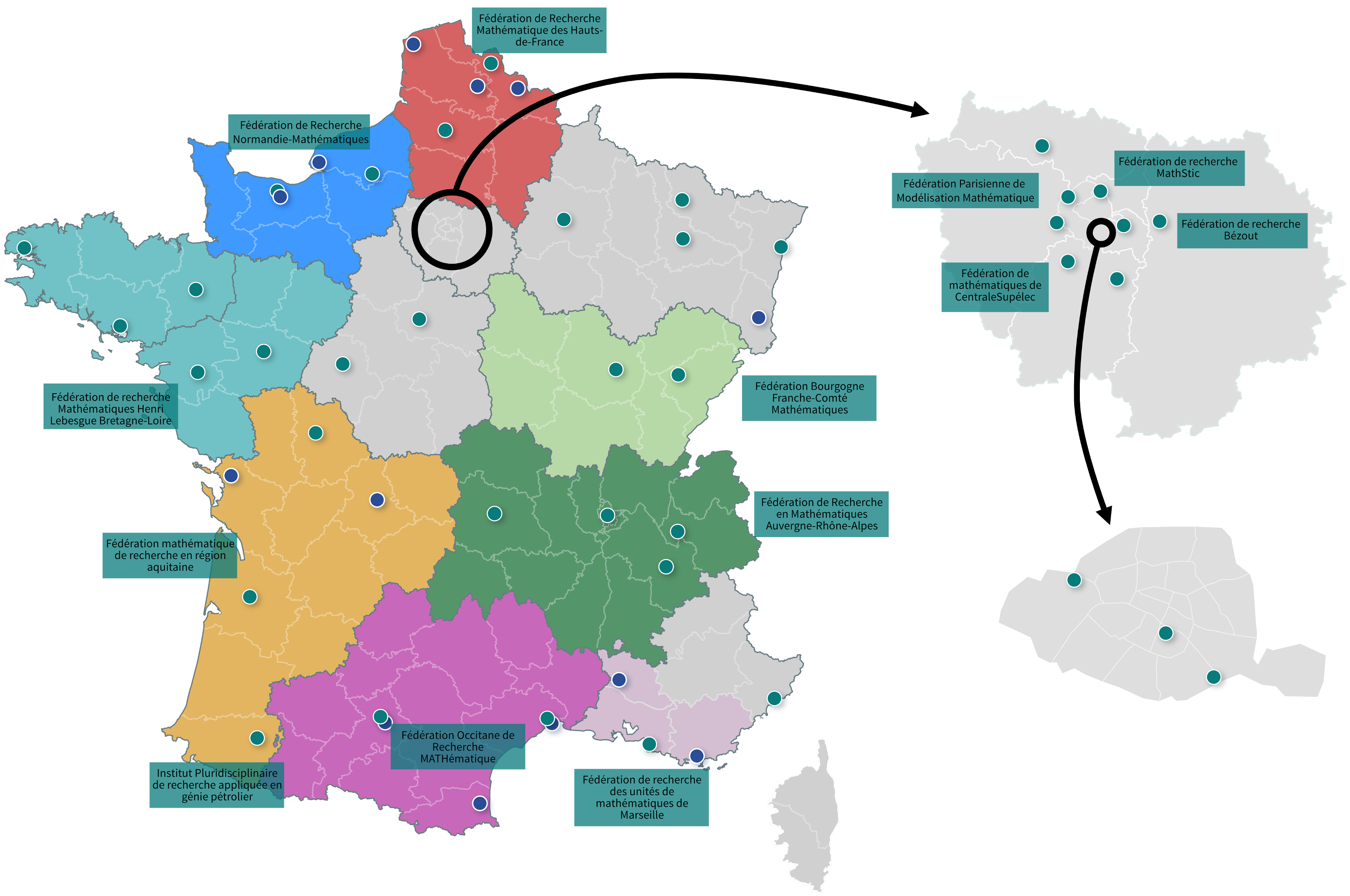
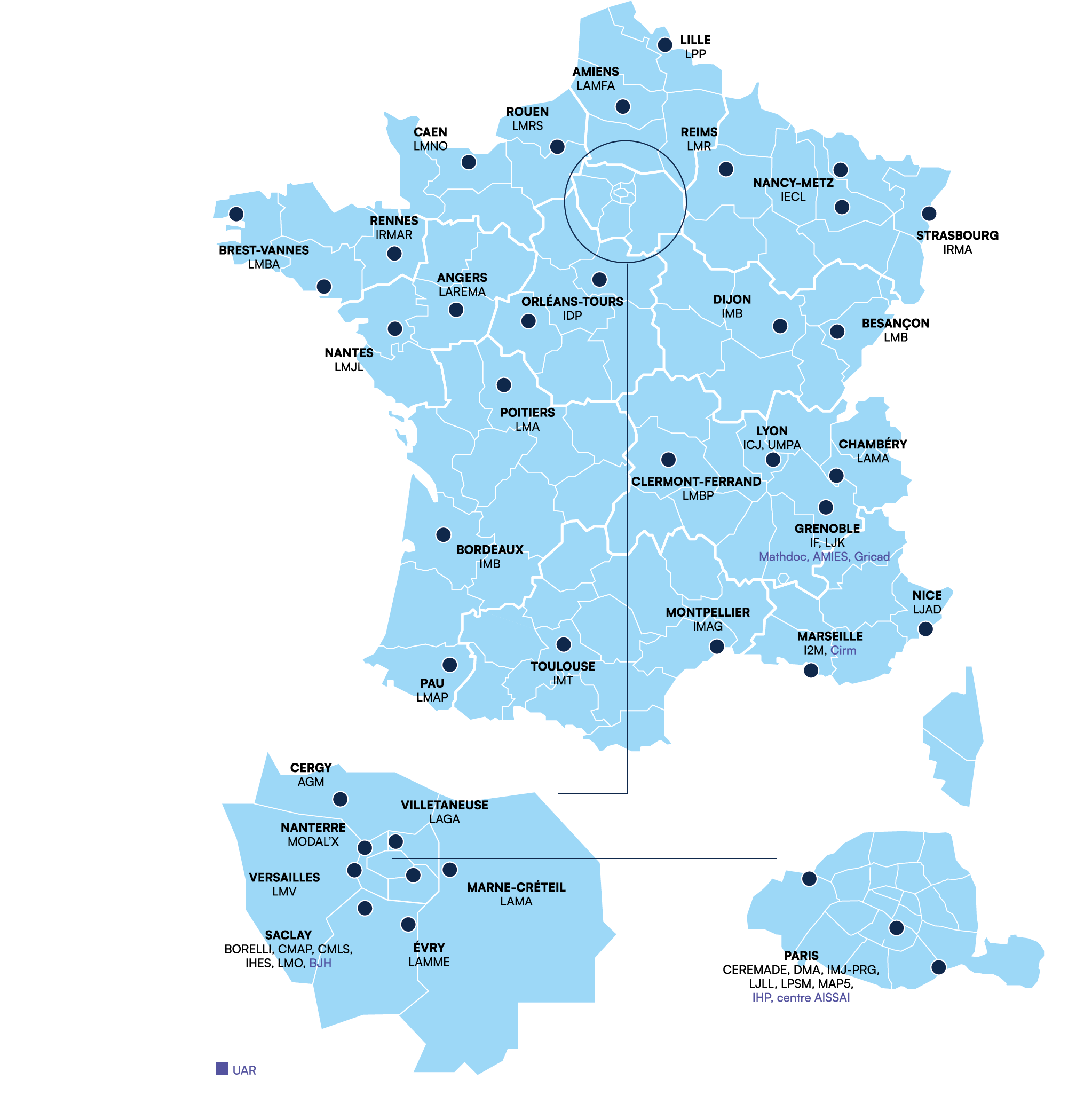
France benefits from a wide range of research structures that complement each other: CNRS laboratories, host units, networks of all kinds, national programmes, etc. The Insmi's mission is to structure the French mathematical community and work towards its integration into the international community.
Mathematics laboratories are mainly university laboratories or laboratories linked to the grandes écoles, and receive financial support from the universities (or grandes écoles where appropriate) and the CNRS. The FrenchNational Research Agency (ANR) also provides funding for various projects. In addition, as part of the future investment programme (PIA), the French government has launched a labelling programme called "Laboratoires d'excellence (LabEx)".
Finally, two foundations, the Fondation sciences mathématiques de Paris (FSMP) and the Fondation mathématique Jacques Hadamard (FMJH), provide funding from both public and private sources, and both host a LabEx.