Taking on the Great Mathematical Conjectures
CNRS News looks at a few of history’s most famous mathematical conjectures, some of which remain unproven and continue to stimulate research.
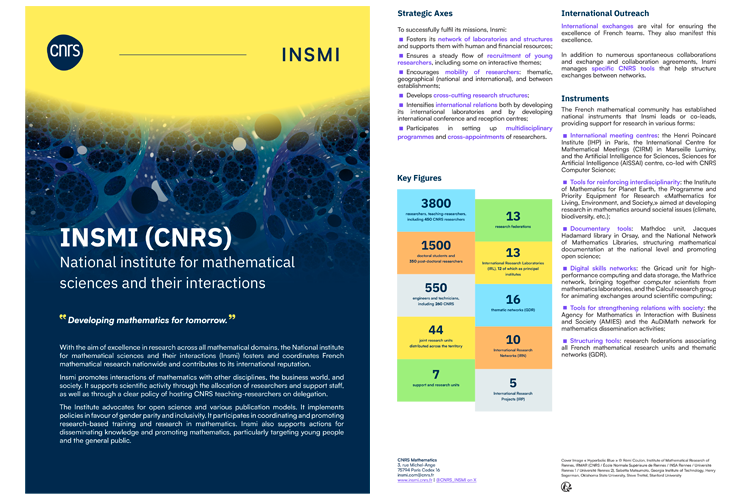
The Insmi's mission is to structure and coordinate the development of research in the different branches of mathematics. The yielded works find an echoe in today's society and serve as a reference at an international level.

In order to carry out its missions, the Insmi regularly recruits young researchers, both in its core discipline and in areas of research that interact with other sciences. It also encourages them to move between different institutions and internationally.
This commitment to openness is reflected in the establishment of cross-disciplinary thematic research networks, support for international conference and host centres, and interaction with the business world and society. Building on the worldwide reputation of its researchers, Insmi is also committed to intensifying international collaboration.
These initiatives bring their own dynamic to the existing network of mathematics laboratories. This network is geographically distributed across the country, with each major regional centre offering scientific expertise that generally covers the entire spectrum of mathematics.
The Insmi is committed to supporting researchers in their work by providing them with national research support structures in the areas of computing, IT resources, documentation, scientific publishing and the dissemination of science.
As is the case for all CNRS institutes, the Insmi's development policy and its strategic choices are informed by the CNRS National Committee, in particular by the Institute's Scientific Council (CSI), a think-tank and forward-looking body, as well as by section 41, interdisciplinary commission 51, and possibly other sections or interdisciplinary commissions.
The Insmi's primary role is to support research in mathematics, in all its varieties, from the foundations of the discipline to interactions with other sciences.
Computer science, epidemiology, genomics, oncology, geophysics... The interfaces with other sciences are numerous. They are the subject of joint subjects where different approaches contribute to mutual enrichment and the advancement of knowledge.
At the same time, the Insmi responds to the growing demands of the business world for modelling, quantitative analysis and simulation, and supports initiatives to promote mathematics to the general public, particularly young people.
CNRS News looks at a few of history’s most famous mathematical conjectures, some of which remain unproven and continue to stimulate research.
Pendant le pic de Covid-19, l'organisation des équipes médicales s'est révélée cruciale.
In coordination with the Mission pour la place des femmes au CNRS, and in partnership with the national association Femmes et mathématiques and the Fondation Blaise Pascal, the Insmi has made parity a priority in its human resources policy. Although women now supervise 30% of theses in mathematics, they hold only 20% of positions as mathematicians, professors, lecturers, directors or research fellows.
At global level, the International Mathematical Union is committed to working with women mathematicians, in particular through the Committee for Women in Mathematics (CWM), which organises various initiatives to promote mathematics among women and women in mathematics. At European level, the European Women in Mathematics (EWM) is active in these areas.
Parity/equality in mathematical research
This Insmi website, dedicated to parity, provides data on staff numbers and recruitment, as well as resources for further reading.